"The Future of Emerging Europe" presents a multifaceted approach to discussing the future of the region, delving into innovation, entrepreneurship, and sustainability. It focuses on five critical dimensions: people, prosperity, planet, partnership, and peace.
"Emerging Europe must adopt the best practices, proven and trusted educational techniques at all levels - from preschool to lifelong learning. It must use the knowledge of Estonia, which has so far developed the most successful education system in the region," the report states.
The key points of Emerging Europe are related to education, digital transformation, addressing the demographic decline of the region, insistence on leading the defense of Europe, and protecting and advancing the region.
A NATO member and EU hopeful,since weathering the consequencesof a major earthquake in 2019 andthe Covid-19 pandemic, the focus ofthe Albanian government is currentlyon full recovery with special attentionbeing paid to tourism, agriculture,and digitilisation.
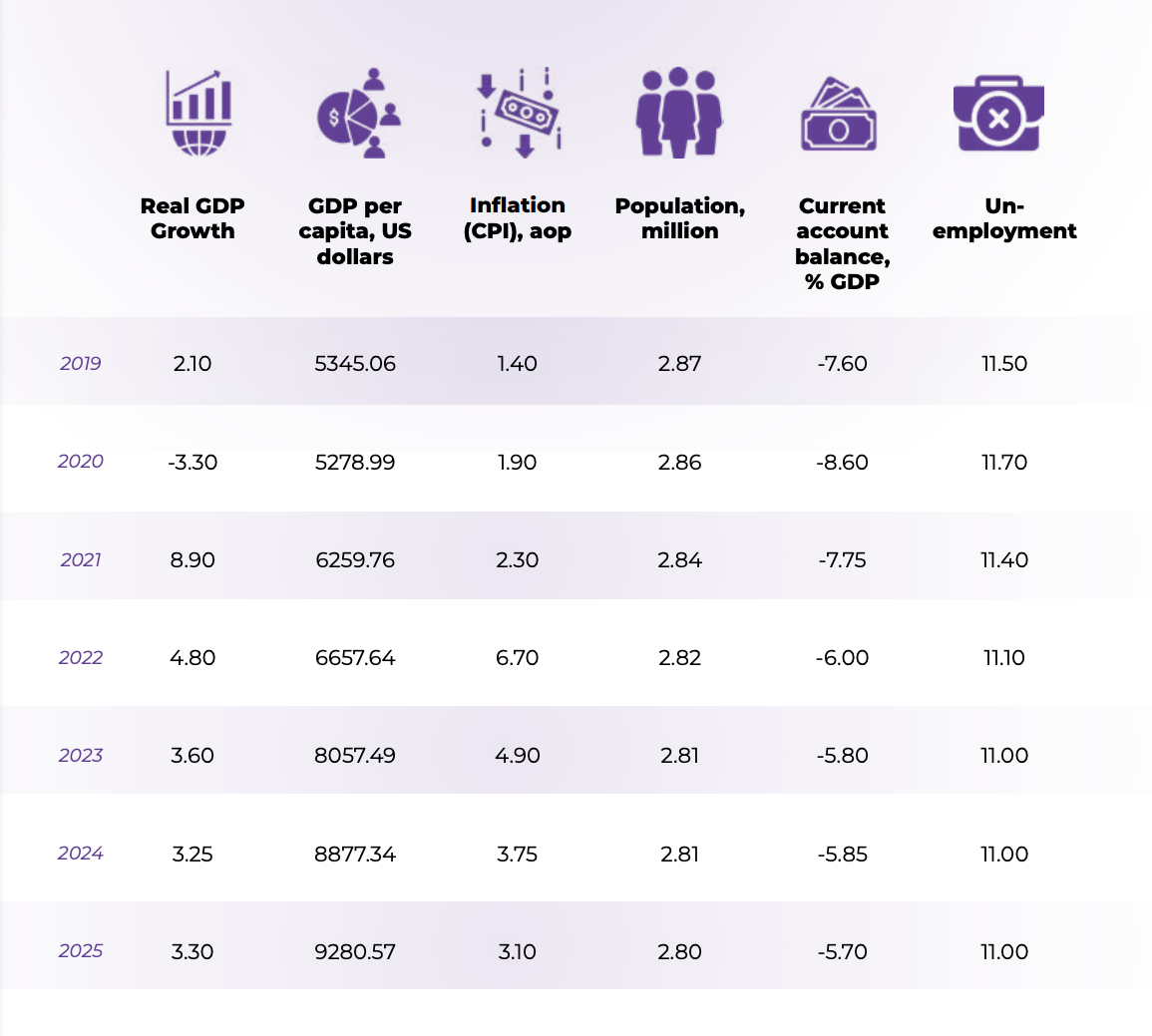
According to the World Bank, in2022, growth reached 4.8 per centas private consumption, exports,and investment increased despiterising energy and food prices. Growthis expected to have moderated to3.6 per cent in 2023, in the contextof tight global financial conditions,limited economic growth inEurope, and the completion ofpost-earthquake reconstructionprogrammes.
Tourism and constructionare expected to drive exports,consumption, and investmentgrowth at rates similar to prepandemic levels. The inflation rate isprojected to start converging towardits three per cent target by 2024.
Poverty is expected to continue todecline as employment and wagesrise. The medium-term prospectshinge on global recovery, structuralreforms, and fiscal consolidation.
Further increases in food and energyprices are a key risk to growth, asthey could affect real disposableincome, slow poverty reductionand potentially constrain the fiscalspace. As a small, open economy,Albania is highly exposed to externalshocks, such as a recession in Europeor further tightening of financingconditions in international capitalmarkets beyond the current year.
GDP growth is set to slow further in2024 to 3.1 per cent, according to theEuropean Union’s Autumn EconomicForecast. Decelerating employmentgrowth is set to weigh on privateconsumption while investmentgrowth is projected to deceleratefurther, to 3.3 per cent, in responseto weakening external demandand rising input costs, and despitesupport from FDI inflows and severalongoing infrastructure projects.
However, service exports areexpected to remain largelyunaffected by the slowing economicperformance of trade partners, astourism to Albania remains relativelycheap and the expansion of itstouristic offer and infrastructure isincreasing its attractiveness.
Reaccelerating private consumptionand investment could raise economicgrowth to as high as 3.7 per centin 2025, although other estimatessuggest more modest growth of 3.3per cent.
You can find the full report here.
0 comments